There are several benefits that are associated with rotational molding that make it so preferable in making a huge range of plastic products. However, it is important to understand that rotational molding is not suitable for making all kinds of parts. As such, before you settle on a given process, you need to start by understanding the various processes for manufacturing plastics that are in existence. In this article, I will discuss the uses of rotational molding and the process itself and reserve the advantages and disadvantages for another article in this series of articles about plastics rotomolding.
Rotational molding uses
Rotational molding also goes by a few other names such as rotomolding and plastic rotomolding. This process is a method that is used in molding thermoplastic products. It is most suited for use on large, one-piece hollow products and products that have double walls and open at one end or either ends. Such products include coolers, kayaks, and tanks among many others. This process is most suitable for production volumes of less than three thousand units per year. Thus, this makes this process suitable for small businesses, start-ups, and investors.
This process is very suitable for manufacturing parts that need high-quality finishes and wall thicknesses that are uniform. Also, this process can be used for parts that need a high level of stability. After a part is made using this process, it is possible to incorporate spin weld attachments and inserts directly into the rotomold. After the insertion is done, thermal insulation and stiffness can be created using foaming. You won’t find weld lines or pinch-off seams in the finished product because there is no need for secondary processes to be applied on the product ones it is completed.
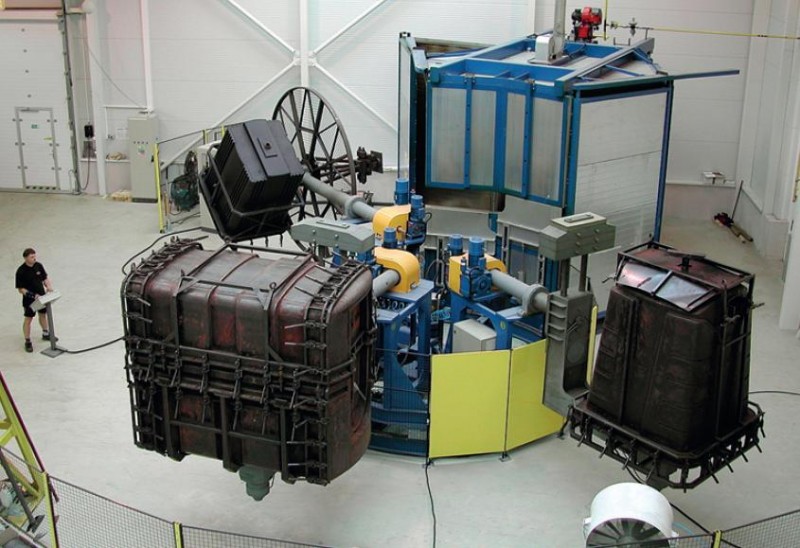

Rotational molding process
The process of rotational molding is very simple. In fact, it is simpler that most people actually imagine. The process starts with a powdered resin being filled into a hollow mold. The mold is then inserted into an oven before it starts to be rotated bi-axially. The mold continues to be rotated as the polymer melts and forms a coat around the mold. Once the polymer has been applied to completion, it is cooled so that it can harden. Once it hardens, it forms the desired shape. The mold is the opened to remove the finished product.
The process involves the use of a combination of high-heat and low-pressure and as such, rotomold tooling is often created out of soft metal like aluminum. Polyethylene is the most commonly used plastic because it has low chemical degradation when it is exposed to heat. Secondary processing or in-mold methods are used to incorporate foam reinforcements, undercuts, kiss-offs, ribs, and inserts among others.
Last words…
Rotational molding is not very suitable for making small products that have complicated shapes and features. The inability to produce complicated shapes makes one of the major shortcomings of this method of manufacturing plastic parts. However, if you want to manufacture large parts, then you know which process to go for.